Dementia & Adiponectin-APN
🎁 SPECIAL GIFT SUMMARY..! ✔Adiponectin is associated with Anti-Neuroinflammatory effects and Improved Cognitive Function in the Brain.

KEY POINTS
Adiponectin (APN) is one of the most abundant and Multifunctional Adipocytokines, with Cardioprotective Effects in Multiple Diseases.
Research has shown that APN has Anti-inflammatory effects, regulatory functions on Glycogen Metabolism, Inhibiting Insulin Resistance (IR), and Anti-Atherosclerosis effects.
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Vascular Dementia (VD) share “Extremely Similar Vascular Risk Factors”, and all of them are closely related to Adiponectin.
Adiponectin Receptors exist throughout the Body and have been found in the Brain, at the level of the Hippocampus and the Hypothalamus.
The Beneficial Influence of Adiponectin on Dementia (AD) is related to the Decreased Aβ-amyloid Deposition and the Inhibition of Tau Tangles.
🎁 SPECIAL GIFT SUMMARY….!!
SUMMARY
Background
Dementia is a growing Global Health Crisis, affecting over 43.8 million individuals Worldwide, with projections suggesting this number could triple by 2050.
- Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Vascular Dementia (VD) have the First and Second place with the 60% and 30% respectively of all Dementia cases.
- This increasing prevalence in Dementia is mostly among Aging people, representing a great socio-economic burden for families and healthcare systems.
- Research has been shown, both Alzheimer's Disease - AD and Vascular Dementia -VD share Common Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Clinical features, including Metabolic Dysfunction.
- Current research considers that Adiponectin (APN), one of the most prevalent and Multifunctional Adipocytokines, is associated with Anti-inflammatory processes, regulation of Glycogen Metabolism, decreased or mitigated Insulin Resistance (IR), and Anti-atherosclerotic effects.
- This review explores the relationship between Adiponectin (APN) and Dementia, addressing the Pathophysiological Mechanisms associated with, and the Pleiotropic Effects of APN, intending to suggest possible therapeutic targets and future research strategies.
Adiponectin (APN)
Adiponectin (APN) is the Most Widespread Adipocyte-derived hormone, and its levels are inversely correlated with Adipose Tissue Dysfunction.
APN has Three (3) Receptors widely distributed throughout the body, and exerts its actions by binding to these receptors, AdipoR1, AdipoR2, and T-Cadherin, which have different biological activities in the body.
The Receptors for the APN actions are distributed on different tissues, such as Adipose Tissue, Skeletal Muscle, Liver, Pancreas, Heart, and Blood Vessels. APN Receptors also exist in the Brain, Hippocampus, Hypothalamus, and Brainstem.
Adiponectin is involved in the regulation of Fatty Acids, Glucose Catabolism, and Cellular Sensitization to Insulin. In addition, APN exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects by Decreasing the production of diverse Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines.
Research has repeatedly reported that Adiponectin is Negatively correlated (has lower levels), with Insulin Resistance (IR), Obesity (BMI), Diabetes (DM2), and Cardiovascular Disease. All of these Factors can Increase the Risk of Dementia.
Furthermore, Adiponectin exerts a Beneficial Influence on Alzheimer's Disease, which is related to the Reduction of Aβ-amyloid Deposition and the Inhibition of Tau Tangles.
The Anti-neuroinflammatory Effects of Adiponectin have been repeatedly demonstrated in diverse Research, playing a Chronic Anti-inflammatory Role in Dementia and other related Chronic Diseases, such as DM2, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Cancer.
In sum, ADPN plays a Multifaceted Role in the Brain, due to its influence on Energy Homeostasis, Neuroprotection, and Cognitive Functions, through its receptors and signaling pathways.
- Its DEFICIENCY is linked to Cognitive Decline and Neurodegenerative Changes, Highlighting its potential as a Therapeutic Target for conditions like Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease.
Dementia
Dementia is characterized by a range of Cognitive Impairments, including memory loss, language difficulties, and changes in personality and behavior, which severely affect daily living activities.
- Among the various forms of Dementia, Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Vascular Dementia (VD) are the most prevalent, accounting for 60% and 30% of cases, respectively (Alzheimer's Disease International Statistics).
- Alzheimer's Disease (AD) symptoms can often be mistaken for Normal Aging, yet established diagnostic criteria exist. Neuropathological features of AD include Amyloid-β Deposits and Hyperphosphorylated Tau Tangles.
- On the other hand, Vascular Dementia (VD) is the result of reduced Cerebral Blood Flow, which significantly Affects Cognitive and Executive Function, and its accurate diagnosis relies on Clinical Symptoms, Neuropsychological Assessments, and Neuroimaging.

- Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Vascular Dementia (VD) Share Common Risk Factors for Dementia, such as Obesity, Hypertension, Diabetes, and Hyperlipidemia. This underlines the importance of understanding the Mechanisms that contribute to their development and the effects of Adiponectin on them.
Regulation Mechanism of Adiponectin on Dementia.
Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia are distinct diseases with potential overlapping Metabolic Dysfunction.
- Therefore, the Pleiotropic Effects of Adiponectin may benefit Alzheimer's (AD) and Vascular Dementia (VD), involving Anti-inflammatory and Insulin-sensitizing effects, regulating Glucose and Lipid Metabolism, and improving Mitochondrial Dysfunction.
- In addition to its Anti-neuroinflammatory effects, the actions of Adiponectin also Benefit Alzheimer's Disease by Reducing Aβ-amyloid Deposition and Inhibiting Tau Tangles.
Mechanisms Linking APN to Dementia
Adiponectin is associated with Dementia through several mechanisms.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: APN exerts Anti-inflammatory actions by reducing the production of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines such as Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α).
- Regulation of Insulin Resistance: APN is known to Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Reduce Insulin Resistance (IR) in both the Brain and Peripheral Organs.
- Impact on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: APN helps in mediating hepatic glucose production and maintaining Glycogen Homeostasis in the Brain.
- Reduction of Amyloid-Beta Accumulation: Research indicates that APN can suppress Amyloid-β (Aβ) accumulation, a hallmark of Alzheimer's Disease (AD).
- Vascular Health Improvement: APN promotes Nitric Oxide (NO) production, which enhances Vasodilation and Improves Cerebral Blood Flow.
- Regulation of Lipid Profiles: APN is associated with Elevated levels of High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) and Low levels of Triglycerides (TG). This Lipid Profile is Beneficial for Cardiovascular Health, which is closely linked to Brain Health and the Risk of Dementia.
- The above mechanisms show the Influence of APN on the Pathophysiology of Dementia and Highlight its potential as a Therapeutic Target to prevent or control associated Cognitive Decline.
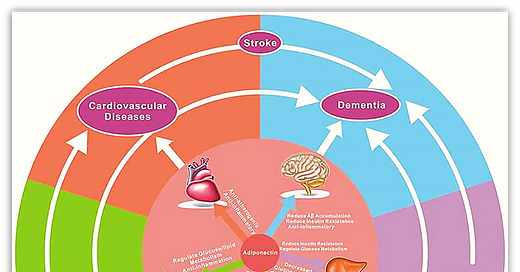
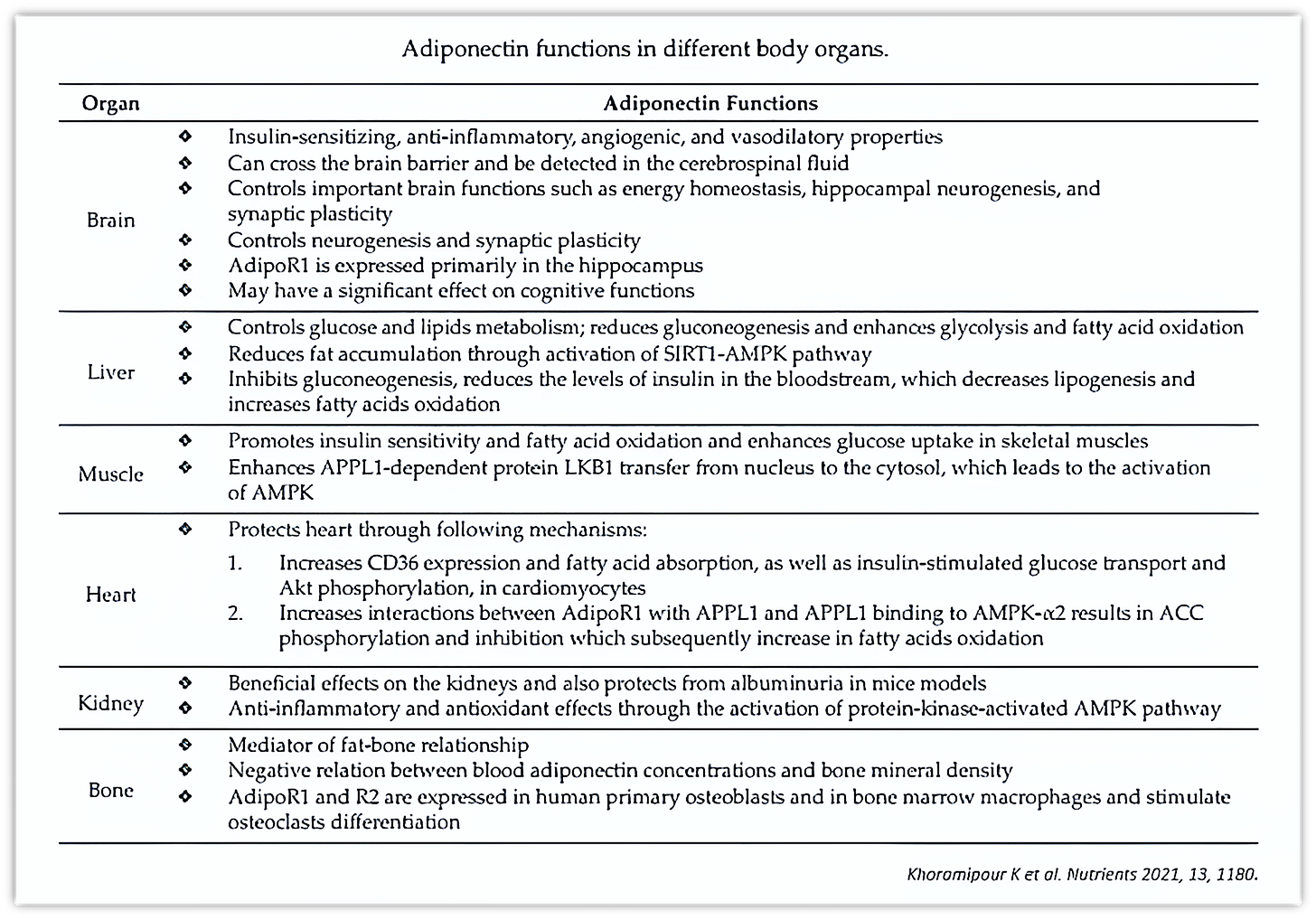
Below are the different FUNCTIONS OF ADIPONECTIN in various organs of the body. * See the effects of Adiponectin on the BRAIN at the Top of the following list.
As shown in the IMAGE ABOVE and the MAIN TOP IMAGE, Adiponectin has Pleiotropic Effects on numerous Organs, and whose Diseases are closely related to each other, since they Share the Same Risk Factors in their Physiopathology.
- For example, Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Diabetes, and Obesity are Risk Factors for Dementia and Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), while Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, and Obesity are associated with the Development of Diabetes.
Adiponectin and Multiple Risk Factors of Dementia
In this Review, the Authors address a number of important Risk Factors, including Hypertension, Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, Midlife Obesity, Atherosclerosis, Stroke, and others, in the Development of Dementia.
It is also shown how AD and Vascular Dementia (VD) share Common Risk Factors, especially Vascular Risk Factors, which indicates a Correlation, and Potential Interaction, between Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Pathology.
This emphasizes the importance of identifying and mitigating these Risks for Dementia Prevention.
The IMAGE BELOW shows the Shared Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia. *See ´Vascular Risk Factors´ >
Adiponectin in Aging
- The incidence of Dementia increases significantly with age, particularly after 65 years. Aging is characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and metabolic decline.
- Age-related Metabolic Disorders, including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease, are associated with Low levels of Adiponectin. APN may play a critical Benefit Role in the Aging Process by Improving Insulin Sensitivity and Reducing Inflammation.
Other Risk Factors
Other Crucial Factors Influencing the Progression of Dementia are also addressed in this Review. As the Genetics, ethnicity, smoking, physical activity, social engagement, cognitive training, diet, traumatic brain injury, depression, sleep, and level of education.
Distinguishing and Utilizing these Modifiable Risk Factors could help us find effective interventions to Prevent Dementia at the Preclinical Stage.
- Finally, the authors point out, that Understanding the Role of APN in Dementia Progression is Key to exploring novel strategies and controlling its development.
*References at the bottom.
If you like this Summary, you might be interested in these Topics related to Dementia and its Risk Factors like Nutrition, Obesity, and CVD. Just CLICK on the image to read the article >
Adiponectin, Leptin, and Resistin and the Risk of Dementia
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ: An Update on Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Microenvironment
Prague Med. Rep. 2015, 116, 87-111 https://doi.org/10.14712/23362936.2015.49

Sources »
Primary Source »
Chen R et al., (2020) Links Between Adiponectin and Dementia: From Risk Factors to Pathophysiology. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:356. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00356
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00356/full#h4Image »
“Adiponectin functions in different body organs”. Khoramipour K, et al. Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition. Nutrients. 2021; 13(4):1180. doi.org/10.3390/nu13041180
👇 Please read this Notice about our NEW PRECARMED Summaries & Notes 👇
📌 THIS SUMMARY YOU ARE READING IS JUST A ´SAMPLE´ 🎁 which already contains some changes and improvements that will be gradually added to your PRECARMED Summaries & Notes (PS & Notes), so there are more on the way….!
- This is a New Private Section, Exclusive for Collaborators and Donors, which will be sent directly to their Inbox...For Free...! 📫📫
- We want to offer our Collaborators a New Exclusive Section that is as fluid, simple, and user-friendly as possible so that you can enjoy reading it.
- PRECARMED Summaries & Notes are not like the usual summaries. You will read an extensive and reliable Summary, enjoying your reading in a friendly format, with resources, illustrative videos, and images that represent the concepts of the summary. This will make your reading more enjoyable and help retain the information in your Brain.
- In addition, we have included in each of the Summaries, several interesting articles related to the Summary Topic, that you can read with just a CLICK, so you will have various options to expand and enjoy your reading, without leaving your area of interest...!!
Visit our ´ABOUT´ Section to learn the 'Why' of our format and the intent of our Precarmed Summaries & Notes > https://precarmed.substack.com/about
🔽 Please CLICK BELOW if you wish to Collaborate, and Subscribe Now to receive our New Private Section, Exclusive for Collaborators, directly to your Inbox...For Free...! 📫📫 👇👇
CLICK ON ANY DONATION BUTTON BELOW, AND YOU WILL BE INSTANTLY SUBSCRIBED > 👇